http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=2288
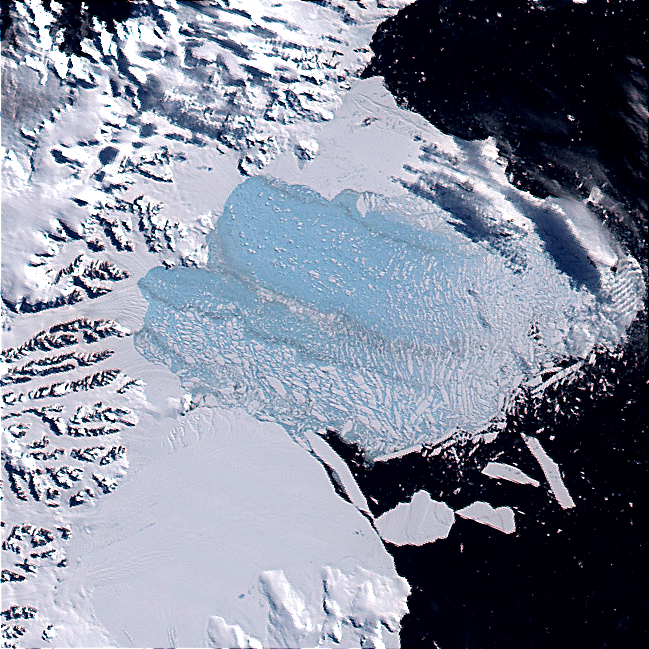
In 2002, the Larsen Ice Shelf, located off the Antarctic Peninsula, was a poster child of the global warming religion, because it fractured (not melted.) This deeply affected the lives of global warming activists everywhere. Note that the open water in the fracture zone immediately refroze.
Over the past decade, temperatures there have been dropping at a rate of about 35ºC per century.

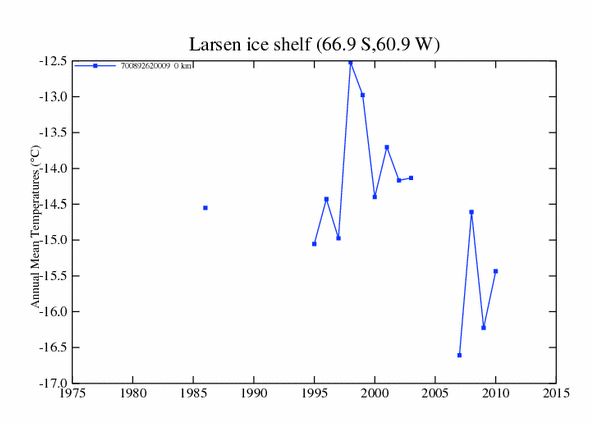

I see it as rising over 20c per century.
That is because you don’t know how to read graphs.
Of course I do, they same way as you.
If I cherry pick the most recent continuous period of data, (2007-2010), it looks like it as rising over 20c per century.
“I see it as rising over 20c per century.”
It’s OK even the experts in climate science read charts upside down every now and then.
According to Mann, it doesn’t matter which way you put the graph as long as he can use it in one of his PCs 😉
Lazarus:
Your monitor is upside down again!
“It fractured not melted”
Are you kidding right? This is the most absurd thing you’ve probably ever wrote. Have you ever looked up the mechanism through which Larsen B disintegrated? It was through meltponds having their warm water penetrate through the ice shelf causing it to fracture. Like really goddard, not a freakin clue eh?
“In the case of the Larsen B, excessive melt water was providing the constant stress needed to push fractures through the ice shelf, which was 220 meters (about 720 feet) thick in places.”
Nonsense
http://www.newscientist.com/article/mg19726433.500-natural-rifts-may-have-weakened-antarctic-ice-shelf.html
There are multiple theories but the melt-pond induced is the most supported by evidence
“One theory is that the build-up of surface melt-water causes initial fragmentation of the ice shelf by downward propagation
of water through crevasses (Scambos et al., 2000; van der Veen, 2007; Scambos et al., 2008; van den Broeke, 2005). The rapid disintegration of the rifted shelves into 15 thousands of small fragments could be explained by a secondary process proposed by MacAyeal et al. (2003). This involves energy being released when narrow ice-shelf fragments capsize in a coherent manner, which then initiate further fragmentation in a
“domino” effect. This mechanism could also help explain the time delay between previous seasons of greatest melt-water build-up and the season of rapid collapse. The 20 pre-break-up surface texture and ice thickness, which are related to the glacier source areas, are also critical in determining the speed of ice shelf disintegration (MacAyeal et al., 2003).”
There are undoubtedly geometric factors which contributed as Glasser and Scambos (2008) pointed out but you should remember that their theory is that the collapse had structural weakness playing a large part in it because of ice shelf frontal retreat caused by warmer air/sea temperatures… It is important to read the fine print you know, sometimes when you actually read the articles you cite then you actually realize it doesn’t support your preconceived notions of skepticism.
By the way, great overview is Cook and Vaughan 2009. The cryosphere
just curious have you checked the average ambient air temperature over the period that hte section of ice shelf separated?
Ice does not have very much tensile strength, so eventually regardless of how thick it is the tidal and wave action will snap off an extended piece , regardless of how thick it is, a moment arm multiple miles long creates a huge amount of stress at the fulcrum.
Given that it immediately refroze, I’m guessing it was below the freezing point. ;^)
And all that leaves out Tidal influences caused by gravitational shifts due to influence from solar and lunar positions relative to locations on the surface of the earth. It has been shown that solid ground bulges with the location of the moon.
If you take normal glacial activity and add tidal influences to the mix you get occasional break ups of ice sheets over the water. Natural movement of glaciers result in deep fissures that can fill with surface melt.
What warmed the water of the melt ponds?
Your medication needs to be adjusted Robert!
There is plenty of evidenceto suggest that the Larsen ice shelf only dates back to the LIA and that that part of Antarctica has for the most part been warmer than now prior to the LIA.
http://www.co2science.org//articles/V9/N50/C1.php
Paul:
You are talking about a period of “prehistory” that is only evident in real unmodified historical records. I believe the current accepted definition for long term is 150 years but may be 30 years as some seem to refer to climate being defined by 30 years worth of records. When climate is the average of long term weather patterns.
If I got it correct Prehistory refers to any time before satellites or in some cases before certain people were born! 😉
lol, “This deeply affected the lives of global warming activists everywhere.”, and obviously many are still scarred from that traumatic event! It was even worse than when the glacier calved and iceberg in Greenland! (Which, as we all know signaled the beginning of end times as we know it!)
I can hardly sleep at night because of worries about icebergs around Greenland.