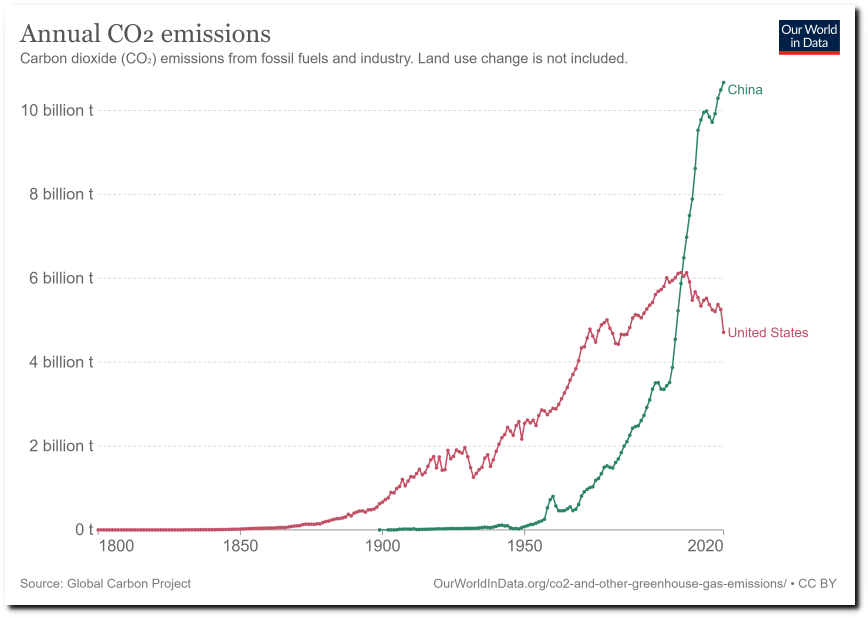
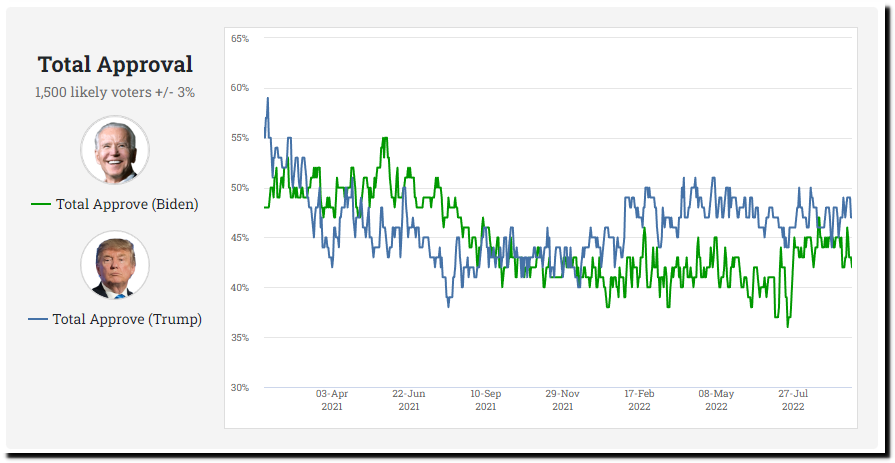
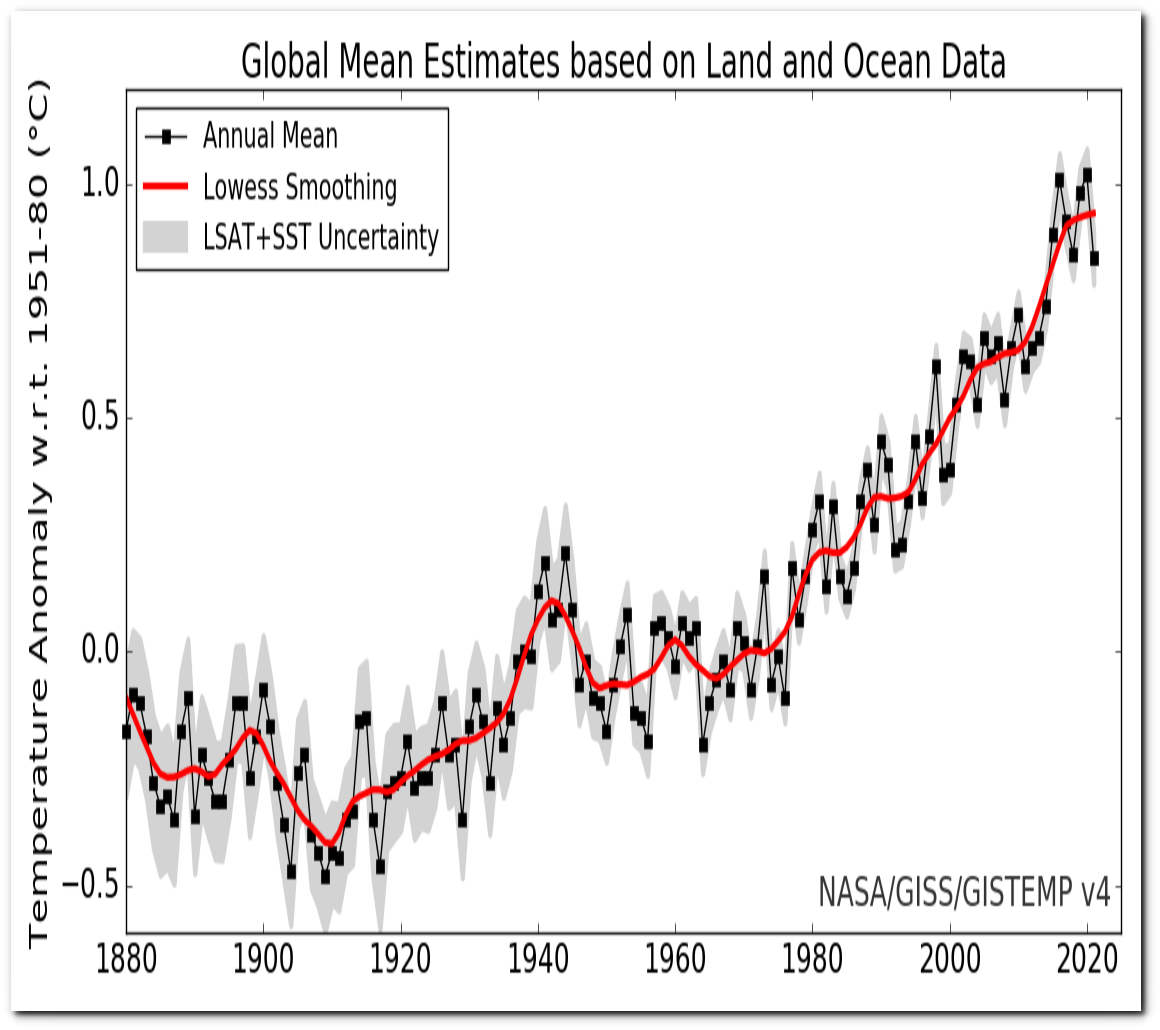
Fifty years ago flooding in Pakistan was blamed on global cooling, but now it is blamed on global warming.
Disrupting the Borg is expensive and time consuming!
Google Search
-
Recent Posts
- Analyzing The Western Water Crisis
- Gaslighting 1924
- “Why Do You Resist?”
- Climate Attribution Model
- Fact Checking NASA
- Fact Checking Grok
- Fact Checking The New York Times
- New Visitech Features
- Ice-Free Arctic By 2014
- Debt-Free US Treasury Forecast
- Analyzing Big City Crime (Part 2)
- Analyzing Big City Crime
- UK Migration Caused By Global Warming
- Climate Attribution In Greece
- “Brown: ’50 days to save world'”
- The Catastrophic Influence of Bovine Methane Emissions on Extraterrestrial Climate Patterns
- Posting On X
- Seventeen Years Of Fun
- The Importance Of Good Tools
- Temperature Shifts At Blue Hill, MA
- CO2²
- Time Of Observation Bias
- Climate Scamming For Profit
- Climate Scamming For Profit
- Back To The Future
March 2026 M T W T F S S 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 Recent Comments
- arn on Analyzing The Western Water Crisis
- conrad ziefle on Analyzing The Western Water Crisis
- conrad ziefle on Analyzing The Western Water Crisis
- Bob G on Analyzing The Western Water Crisis
- Gordon Vigurs on Analyzing The Western Water Crisis
- Bob G on Analyzing The Western Water Crisis
- Bob G on Analyzing The Western Water Crisis
- Bob G on Analyzing The Western Water Crisis
- Mike Peinsipp on Analyzing The Western Water Crisis
- Bob G on Analyzing The Western Water Crisis